Windows Server 2022 vs 2019 vs 2016 – What’s the Difference
Windows Server 2022 vs 2019 vs 2016 – What’s the Difference. This article discusses the key differences between Windows Server 2022 vs 2019 vs 2016.
Due to popularity of remote work and cloud storage, organizations may find it worth upgrading to the new OS, due to new features and improved security. Microsoft typically has a ten year support cycle for its Windows Server operating systems. With the Windows Server 2012 R2 End of Life deadline around the corner (10 October 2023), many organizations will look to upgrade. While it is always a good idea to upgrade to the latest version, it is not always necessary or financially feasible. As such, organizations must carefully weigh their options before finally committing.
Microsoft has three server operating systems that (at the time this article was published) were at least under extended support. The following guide will examine these operating systems and help you decide which one will be best to use for your network infrastructure.
Let’s start our comparison of Windows Server 2022 vs 2019 vs 2016.

Microsoft Windows Server 2022
Since Windows Server 2022 is the latest release, it will be the first to get covered on our Windows Server 2022 vs 2019 vs 2016 guide. It is the tenth major release of Microsoft’s series of operating systems for servers. Windows Server 2022 continued Microsoft’s 3-2-year major release cycle. As with previous versions, Windows 2022 follows Microsoft’s LTSC model. It offers five years of mainstream support and five years of extended support starting from the 2nd of November 2021.

Windows Server 2022 is said to be the most secure iteration of the OS, thanks largely to its advanced multilayer security features including:
Windows Server 2022 New Features
- Firmware attack prevention through Dynamic Root of Trust for Measurement (DRTM) and Direct Memory Access (DMA).
- Hypervisor security through virtualization-based security (VBS).
- Secure connectivity enforced through Transport Layer Security.
- Server Message Block (enforced through Quick UDP Internet Connections).
-
- Windows Server 2022 is updated to further support large-scale operations like SQL.
-
- Improvements to Windows Containers.
However, this is only just one reason you should consider using Windows Server 2022.
Windows Server 2022 Notable Features
Microsoft released Windows Server 2022 with a host of new features, missing from previous iterations of the operating system. Some of the most notable include:
Server and network support improvements
Windows Server 2022’s came with much-needed server management upgrades. It can support servers with up to 48 terabytes of RAM and 2048 logical cores running on 64 physical sockets. Additionally, it is compatible with Intel’s set of 3rd generation Xeon Scalable server processors (Ice Lake SGX).
In regards to network management and support, Microsoft introduced improvements to both the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol. It also introduced virtual switch upgrades and Quick UDP Internet Connections (QUIC) to help speed up connections while keeping them secure.
Improvements to storage management
Windows Server 2022 came out with markedly improved storage management features. It introduced enhanced caching, improved hard drive error checks and repairs, and ReFS file snapshots.
More comprehensive Azure support
Microsoft has always been at the forefront of cloud development. Windows Server 2022 would serve as another testament to this fact. Some of its best highlights include automated VM management, greater .NET application support, improved server management, and enhanced admin center reporting (Windows Admin Support).
Additionally, Windows Server 2022 supports virtualization from third-party vendors and streamlined updates. The multi cloud support features are Storage Migration Service and Azure Arc- the two hybrid cloud tools, that work best in these multi cloud environment.
Improved application support
Microsoft Windows Server 2022 features new optimized updates of container applications. It also has enhanced support for large scale business applications such as Microsoft SQL Server 2022. This is largely due to its ability to accommodate more RAM and new CPU architecture with greater cores.
Additionally, Windows Server 2022 loads 30% faster than its predecessors because of its optimized Windows containers. You can demo some of these features by downloading an official evaluation ISO. While Windows Server 2022 introduces a host of exciting improvements, it does remove a few outdated features from previous iterations.
Windows Server 2022 Deprecated Features
Before you upgrade or purchase Windows Server 2022, you should consider that Microsoft stopped full or partial support for the following features:
Internet Storage Name Service (iSNS)
A protocol that finds and works with Internet Small Computer Systems Interface (iSCSI). Support was removed from Windows Server 2022.
Sconfig
While not completely deprecated, Microsoft has stopped development on the Server Configuration tool and plans to completely remove it from the next iteration of Windows Server. Microsoft encourages users to utilize PowerShell and as such, configured it as the default shell for Windows Server 2022.
Guarded fabric and shielded virtual machines
A feature that allows VMs to run exclusively on guarded hosts. Microsoft still offers partial support in Windows Server 2022. However, it has halted all development on it.
Windows Deployment Services
This feature is partially deprecated in Windows Server 2022. You can no longer install the operating system using Windows Setup using WDS. Additionally, you can no longer launch the Windows installation using boot.wim from an installation media.
Local Security Authority Protocol interface
Again, Microsoft only partially stopped supporting this feature in Windows Server 2022. As such, you can no longer install the operating system using Windows Setup using WDS. Additionally, you can no longer launch the Windows installation using boot.wim from an installation media.
Most of the above features have been deprecated because Windows Server 2022 introduces features that improve upon their functions or they are no longer secure. Nevertheless, as with most Microsoft operating systems, Windows Server 2022 comes in different editions.
Windows Server 2022 Editions
You can get Microsoft Windows Server 2022 in the following editions:
Standard
Windows Server 2022 Standard Edition can be considered the base version. Its primary use cases involve physical servers and/or environments with minimal virtualization. The Standard Edition utilizes a core based licensing model. The $1069 retail price for each license covers up to 16 CPU cores.
Environments that exceed this figure must purchase additional licenses.
Furthermore, each client that accesses a server running the Windows Server 2022 Standard Edition operating system will require a Client Access License (CAL). It allows you to establish a single replication partnership using the Storage Replica feature with up to a 2TB volume. Furthermore, it does not feature support for software defined networking and storage.
Moreover, it supports an unlimited number of Windows Server containers but limits it to two operating systems per license. Thus, only allowing your server to run two operating system environments or Hyper-V virtual machines (VMs)/containers.
Essentials
The Windows Server 2022 Essentials Edition is Microsoft’s most cost effective option. It uses a special server licensing model. Microsoft intends it for SMEs with up to 25 users and 50 devices. Originally, it retailed for $501 (at the time of writing this guide) for a single socket, single VM, and up to 10 cores. Unlike the Standard Edition, it does not require CALs. It is only available through a limited number of Microsoft server hardware partners.
Datacenter
The Windows Server 2022 Data Center Edition is Microsoft’s answer for highly virtualized systems and environments. As such, it’s ideal for well established organizations with large integrated cloud infrastructure. As with the Standard edition, it uses a core based licensing which covers up to 16 cores. Microsoft charges $6,155 per license. Additionally, it requires CALs.
Datacenter Azure
Windows Server 2022 Datacenter Azure Edition is a fairly new entry into Microsoft’s server licensing models. This edition allows you to manage the operating system as either an Azure Stack Hyperconverged Infrastructure (HCI) cluster or VM. Microsoft does not intend if for raw physical machines. Users can be run this edition of the OS as a Hyper-V VM. It offers an exclusive set of features that cannot be found in the other editions of Windows Server 2022.
For a more complete breakdown of some of the above licenses, you can visit Microsoft’s official edition comparison page. It highlights the differences between the Standard, Datacenter, and Datacenter Azure editions of Windows Server 2022 in more detail.
Next in the Windows server blog article about Windows Server 2022 vs 2019 vs 2016 – What’s the Difference is to introduce Windows Server 2019.
Microsoft Windows Server 2019
Upon it’s release, it lacked Microsoft Edge support. Furthermore, it used Internet Explorer 11 as a compatibility layer.
However, it soon added Edge support at the beginning of 2019. Nonetheless, Microsoft Windows Server 2019 would lay the foundation for Windows Server 2022 with a host of new features.
Microsoft Windows Server 2019 Notable Features
You should consider using Microsoft Windows Server 2019 for the following features:
Windows Admin Center
Microsoft had originally showcased it as Project Honolulu during the Ignite Conference in 2017. It’s an all in one administrative tool that uses a modern web interface. Today, it’s considered one of Microsoft Windows Server 2019’s most innovative new features.
Security and storage enhancments
Microsoft included improvements to Windows Defender Advanced Threat Protection and shielded VMs in their release of Windows Server 2019.
They also introduced a few tweaks to how drives were managed. These improvements included new migration services, Storage Space Direct and Storage Replica.
Container services
Windows Server 2019 introduced support for container services such as Tigera Calico, Kubernetes, and Docker. Additionally, it features support for Linux containers.
Improved administrative tools
In addition to the inclusion of the Windows Admin Center, Windows Server 2019 includes new System Insights, easier deployments through SetupDiag, and integrated OpenSSH.
Again, you can download the Windows Server 2019 evaluation copy for free if you want to test-drive some of its features.
Microsoft Windows Server 2019 Deprecated Features
The following features were halted and partially discontinued when Microsoft released Windows Server 2019:
OneSync Service
This background application was originally responsible for syncing data between the Mail, People, and Calendar applications. Windows Server 2019 replaced it with Outlook’s integrated synchronization engine.
Key Storage in Hyper-V
Microsoft halted the development of the Key Storage Drive (KSD) feature due to the obsoletion of generation 2 VMs.
Windows Filtering Platform (WFP) lightweight filter switch
This features was no longer necessary as users could get similar functionality by using full filtering extensions.
Trust Platform Module (TPM) managemetn console
While Microsoft deprecated this feature, users can find the identical functionality and information from the Window Defender Security Center’s Device security page.
Remote Differential Compression (RDC) API Support
This feature allowed for quick compression of data synchronized between remote locations. Microsoft halted development and support for it during the production of Windows Server 2019.
Host Guardian Service Active Directory attestation mode
Windows Server 2016 replaced this feature with host key attestation.
Microsoft Windows Server 2019 Editions
Again, Microsoft Windows Server 2019 was released in a variety of editions including:
Essentials
As with Windows Server 2022, each license covers 50 devices used by 25 users. This aspect makes it a low-priced option for SMEs. The Microsoft Server 2019 Essentials edition features basic Azure Virtual Network integration with seamless network resource mapping. However, some features such as Experience Role functionality, client backup and remote web access are absent from this version.
Standard
The Standard Edition is suitable for physical environments with minimal virtualization. Client machines require CAL. It features basic Windows server functionality. Additionally, it offers basic Azure integration and the Host Guardian Service. However, it does not feature Hyper-Converged Infrastructure, shielded VMs, and software-defined network/storage. Unfortunately, it limits you to two OSE or VM containers per license. Storage Replica is available for the Standard edition of Windows Server 2019.
Datacenter
It’s suitable for considerably virtualized systems such as cloud environments and data centers. This edition offers unlimited OSEs and/or VM containers. It has all the features of the Standard edition. However, it also features unlimited Storage Replica, Host Guardian Hyper-V support, Shielded VMs, software defined networking/storage and hyper-converged infrastructure. The Datacenter Edition is the most complete version of Microsoft Windows Server 2019. Datacenter license cost $6155 upon release.
And last but not least in the article about Windows Server 2022 vs 2019 vs 2016 – What’s the Difference is to talk about Windows Server 2016.
Microsoft Windows Server 2016
With the increasing ubiquity of cloud computing, Microsoft Windows Server 2016 would be more cloud focused. With its release, Microsoft also introduced improved security and Azure integrations. Some of it’s most exciting features included Windows PowerShell 5.1, Windows Server Containers and Nano Server.
Microsoft Windows Server 2016 Notable Features
Windows Server 2016’s other noteworthy features include:
Active Directory (AD) Federation Services (FS) improvements
Users can configure the AD FS feature to authenticate users stored in non active directories in Microsoft Windows Server 2016.
Windows Defender Integration
Microsoft Windows Server 2016 features integrated Windows Server Antimalware. It is configured and enabled by default.
Improved Remote Desktop Services support
Windows Server 2016 features improved remote desktop performance and stability. Additionally, Microsoft added support for OpenCL 1.1 and OpenGL 4.4.
New Storage Services
Microsoft Windows Server 2016 added Storage Replicas and Central Storage QoS Policies.
Web Application Proxy improvements
Windows Server 2016 offers HTTP to HTTPS redirection, Propagation of client IPs address (to backend applications), Pre-authentication for HTTP Basic application publishing, and wildcard domain publishing of applications.
Microsoft Windows Server 2016 Deprecated Features
The following features are partially or fully unavailable in Microsoft Windows Server 2016:
Software Quality Metrics (SQM)
Users can no longer opt-in (or out) of the Customer Experience Improvement Program (CEIP) in Windows Server 2016.
Tablet PC Journal Reader Platform Component
Microsoft removed the journal.dll from Windows Server 2016 and did not replace it.
Share and Storage Management span-in for MMC
While this feature has been removed, users can work around it by using VMs or remoting to operating systems that still support it.
exe /detectnow
A command that triggers scans for updates in PowerShell. You can now initiate updates using the AutoUpdate COM object.
Sconfig.exe
The Sconfig.exe tool no longer exists in this iteration of Windows Server. Users must use the Sconfig.cmd.
scregedit.exe
Microsoft stopped development on configuration through this tool. It encourages the use of reg.exe or PowerShell for configuration scripts that scregedit.exe dependencies.
NetCfG Custom API
Installation of features through NetCfg custom APIs are deprecated but you can still use them. However, Microsoft discourages its use.
SMB 2+ over NetBT
Microsoft encourages users to implement the Server Message Block (SMB) protocol over Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) or Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). It no longer supports SMB 2+ ov NetBT.
Microsoft Windows Server 2016 Editions
Windows Server 2016 features three different editions:
Essentials
Once again, Microsoft Windows Servfer Essentials is best-suited to start-ups and SMEs. It uses a CPU based license that covers a maximum of 25 Users on 50 different devices. Upon release, each license cost $501. Clients did not require CALs.
Standard
The Standard edition offers core based licensing and requires CAL for every client that connects to the licensed Windows server. Because it only supports two OSE or Hyper-V VM containers, it’s only suitable for workloads or environments with very little virtualization. It has a 24TB RAM limit. Additionally, it has a CPU limitation of 512 cores. Microsoft priced licenses at $882 each. Storage management features such as Storage Replica and Space Direct are absent from this edition. Furthermore, it’s missing shielded VMs and a networking stack.
DataCenter
The DataCenter edition is ideal for large virtualized environments. At a price of $6155, it is the most expensive edition of Microsoft Windows Server 2016. It has unlimited OSE and Hyper-V VM containers and has every feature of the Standard Edition and more.
As with other modern versions of Windows Server, Microsoft provides an extensive list comparing the differences between Windows Server 2016 Standard Edition and Datacenter.
Windows Windows Server Family Tree
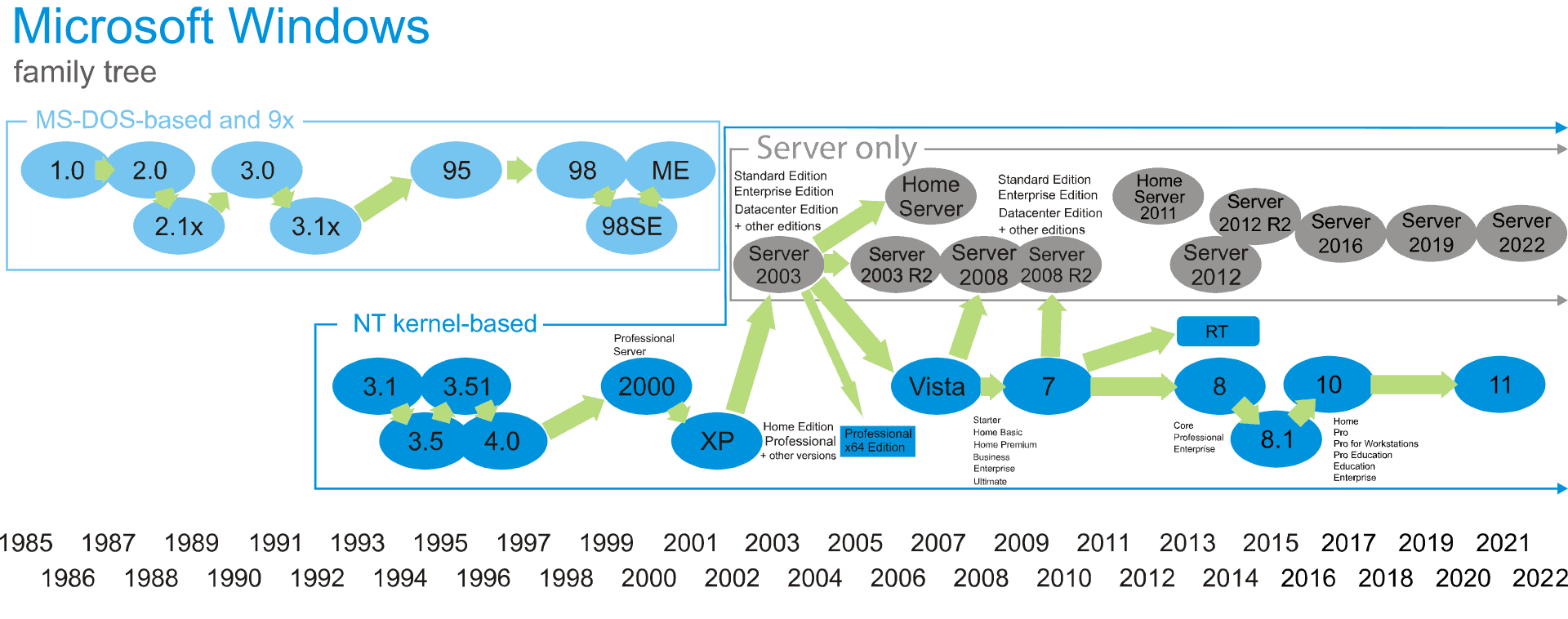
Great effort! We have learned more about Windows Server 2022 vs 2019 vs 2016 – What’s the Difference. Let’s conclude.
Windows Server 2022 vs 2019 vs 2016 – What’s the Difference Conclusion
Windows Server 2022 vs 2019 vs 2016 – all three are important entries in the Microsoft Family Tree. But which should you choose? They are all based on Windows 10. With Microsoft Server 2016’s end of mainstream support rapidly approaching (12 November 2022), upgrading or using one of the latest versions will be vital. However, it’s important to remember that Windows Server 2016 has extended support till 2027. For some, Windows Server 2016 be easier to use and you can potentially find licenses at a reduced rate.
Regardless, it may be tempting to stick with your current version of Windows Server, if it meets all your current organizational requirements. After all, standard and data center licenses can be expensive. However, the increasing number of data breaches and cyberattacks should be concerning. Since Microsoft still supports Windows Server 2016 and 2019, they receive regular security updates and patches. Thus, users who can afford to do so should capitalize on these improvements and upgrade to Windows Server 2022.
Ultimately, ensuring that you’re using a compatible operating system and you have the latest patches are two of the most important practices for Active Directory Security. Furthermore, using Microsoft Windows Server 2022 may allow for smoother cloud migration. However, your hardware infrastructure may not be compatible with the latest version of Microsoft Windows Server 2022. Microsoft Windows Server 2019 offers greater overall security enhancements than Microsoft Server 2016. Additionally, it may offer better stability and performance for your low power hardware compared to Windows Server 2022. Thus, it’s important to examine your network and infrastructure before making a final decision. You should also consider which editions of these operating systems would suit your business requirements. The most scalable solutions are always the best.
Related Posts:
- How to Setup Windows Print Server on Windows Server 2016 / 2019 / 2022
- Windows Server Hardening Security Checklist (Windows 2016 / 2019 / 2022)
- How to Install RabbitMQ on Windows Server 2016/2019/2022 (Tutorial)
- How to Install XAMPP on Windows Server 2016 / 2019 / 2022
- How to Install WAMP on Windows Server 2016 / 2019 / 2022
- How to Install Docker Compose on Windows Server 2016 / 2019 / 2022




