How a Certificate Authority Works
What is a certificate authority?
A certificate authority is known to be a trusted organization that is capable of verifying websites and other related entities. CA plays a major role in digital security, making the internet more secure for users and entities.
What is the role of a certificate authority?
Most of the services are becoming online over time. Think of services like online stores, banking, and other services that use sensitive data to proceed. Since users share a lot of sensitive and private data through web platforms while using these services, there is a potential risk of these data being stolen by hackers. As discussed previously, CAS issues a digital certification to verify websites and other online platforms. Additionally, it allows you to find information about a certificate owner, such as their name, location, and any other details related to their identity.
What does it do?
When you visit a website, if you can see the padlock sign or visit the site over HTTPS, that site is verified by a CA. If you see the “this site is not secure” label, that site is not validated by a CA, or the validation may be expired.
This is basically what a certificate authority does. They verify that you are communicating with the actual websites or organizations and not with a fake entity.
- CA goes through the records captured from official sources and documents to ensure that the online platform you communicate with is a legitimate organization, domain name, or individual.
- CA issues digital certificates which contain vetted and validated information about the respective organization. It provides vouch on companies for the people who do not know the company, whether it is trusted or not.
- CA maintains certificate revocation lists with the details of the certificates that became invalid before the expiry period.
How does certificate authority work?
Now we know that CA certification plays a major role in establishing trust between the users and web pages.
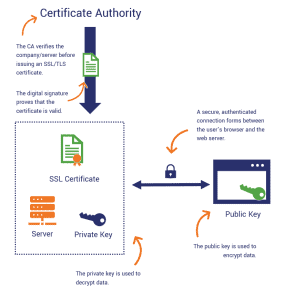
When a user attempts to connect with a website, the webserver sends its public key and the digital certificate verified and signed by a CA. SSL/TLS handshaking establishes this trust with the client party. Once you have this certificate, you can install it on the browser, and then it will allow you to verify the identity and proceed with establishing an encrypted and secured connection between the client and the server. Here, encryption is required to protect the data being transferred between these two from unintended parties. In simple terms, to avoid any kind of hacking.
We will now look into some of the key terms you should be aware of when learning the process of a CA.
Verification
When an organization approaches a certificate authority, that authority follows a verification process according to the requested type of certificate. There are three main types of validation as listed below.
- Domain Validation (DV):
This is the bare minimum of all three validation types. With this validation, the CA verifies that the requested organization is the actual and legitimate managing entity of the subject domain/website.
.
- Organization Validation (OV):
This type of validation lies one step ahead of domain validation. Provided that the domain validation is there, CA performs basic business-level validation with human support. It reviews the information provided by the requestor and also researches some additional information. This also involves other third-party sources. Finally, if all these records are sufficient for the validation process, the CA states that the organization is legitimate.
- Extended Validation (EV):
This is the topmost level of business validation, and this process takes about five working days. There, the CA has to go through the requestor company/entity thoroughly. Undoubtedly, this is beyond the requirements of the organization validation process yet more assured than other validation types..
Digital Certification
After the validation, this is the point where the CA can offer clients a visible identity for their website. We call this a digital certificate, and it helps the browser establish a trusted connection with the website.
A digital certificate is a digital file that contains the critical data as mentioned below:
- Name and other information of the requestor organization
- Public key — This is the half of your public-private key pair that’s publicly known.
- The name of the certificate issuer (name of the certificate authority)
- The digital signature of CA
- A serial number – Unique code to a single SSL/TLS certificate.
- Issued and expiration dates- Certificates are only valid for a given period (up to 398 days)
When a CA issues a new digital certificate, a new record will be created in its public CT logs.
There are multiple categories of digital certificates that can be acquired upon the requirement and the type of web service. However, TLS certificates are the most popular as well as the most focused certificate offered by CA
- SSL/TLS Certificates
- Code signing certificates
- Email certificates
- Document signing certificates
- Device certificates
- User or client certificates
SSL/TLS Certificates
These certificates can implement an encrypted and secured connection between the user’s browser and the organization’s web server. Moreover, they will provide websites with the padlock icon, as we discussed at the very beginning. It can also eliminate the “Not Secure” warning label or kind of “your connection is not private” warnings from a site.
SSL/TLS certificates can be further categorized according to validation levels as mentioned above and also be divided based on their functionalities
- Single domain certificates
These types of certificates secure only one domain. (Both the WWW and not-WWW versions of the same domain are included.)
- Multi-domain certificates
These certify multiple domains and subject alternative names (SAN) such as alternative hostnames, common names, IP addresses, etc., under a single certificate.
- Wildcard certificates
The wildcard SSL/TLS certificate secures unlimited subdomains for one specific domain with a single certificate.
- Multi-domain wildcard certificates
These certificates enable securing multiple subdomains under the same domain name and multiple domains under a single certificate.
Code signing certificates
Developers and app publishers commonly use these certificates to get their code digitally signed. It helps them authenticate the organization and show the users that it’s specifically you, a legitimate organization is trying to tamper and not an unethical act. Having this kind of certification can avoid such warnings when trying to install their products.
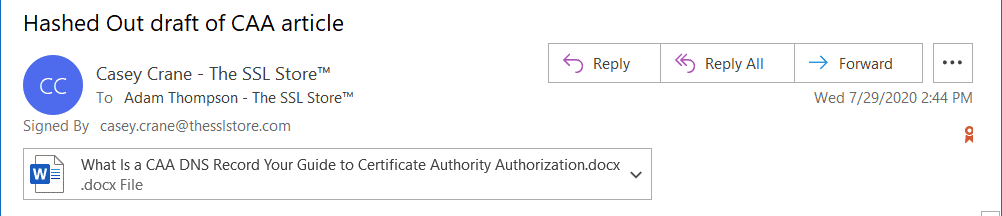
Email certificates
These are useful when authenticating clients to web servers. The signed by tag allows users to see more details about the sender and ensure that it genuinely came from the respective sender/entity.
There are different types of certificates.
Document signing certificates – These are used to authenticate the document creators and validate the content of the document itself is genuine.
Device certificates – This type of certification is mainly used in the IoT (Internet of Things) field to authenticate IoT devices.
User or client certificates – This is another type of certification that CA issues which is basically used to authenticate an individual.
Digital Signatures
CA applies a digital signature to the digital certificate to assure and state two essential factors as the following:
- To prove that a trusted certification authority has issued the certificate.
- To validate that the certificate has not been modified or replaced.
Digital signatures can’t be copied, modified, or faked due to hashing and check-sums methodologies.
Certificate Revocation
The certificate revocation list consists of the certificates that have been blacklisted before their expiry date. CA adds a certificate to this list when there are some issues regarding the relevant entity, and therefore it is no longer trustworthy. This list is accessible to the clients, and even the web servers can access it through the OCSP stapling process.
Types of Certificate Authorities
There are two types of certificate authorities as public and private. A public CA is a third-party entity that is not controlled by any person or an organization. They can issue publicly trusted digital certificates aligning with the regulatory standards.
A private CA is an internal CA that issues certification for its own web services. This type can only be trusted by its internal users, systems, and clients. Here we have to set up a private CA for this having a certificate authority server of their own using active directory certificate services. There are methods to implement root CA or a Subordinate CA with AWS PKI, Azure PKI, GCP PKI and cloud PKI, etc.
Conclusion
CA is similar to an authority who issues you an identity card. It enables companies to authenticate themselves to users providing a digital signature proving themselves a legitimate body. The internet is no longer safe or secure. Therefore it is critical for website owners to have a CA certification not only for them but also for all internet users to clearly understand the risk they are taking when accessing a site that is not verified to be genuine.
Related Posts:
- How to Setup Active Directory Certificate Services (PKI) in Azure, AWS, GCP (Certificate Authority)
- Certificate Enrollment using Active Directory Certificate Services
- Designing a PKI Certification Authority Hierarchy - Best Practice
- Why Do You Need Active Directory Certificate Services?
- How To Deploy Certificates using Active Directory Certificate Services
- Active Directory Certificate Services Best Practices

